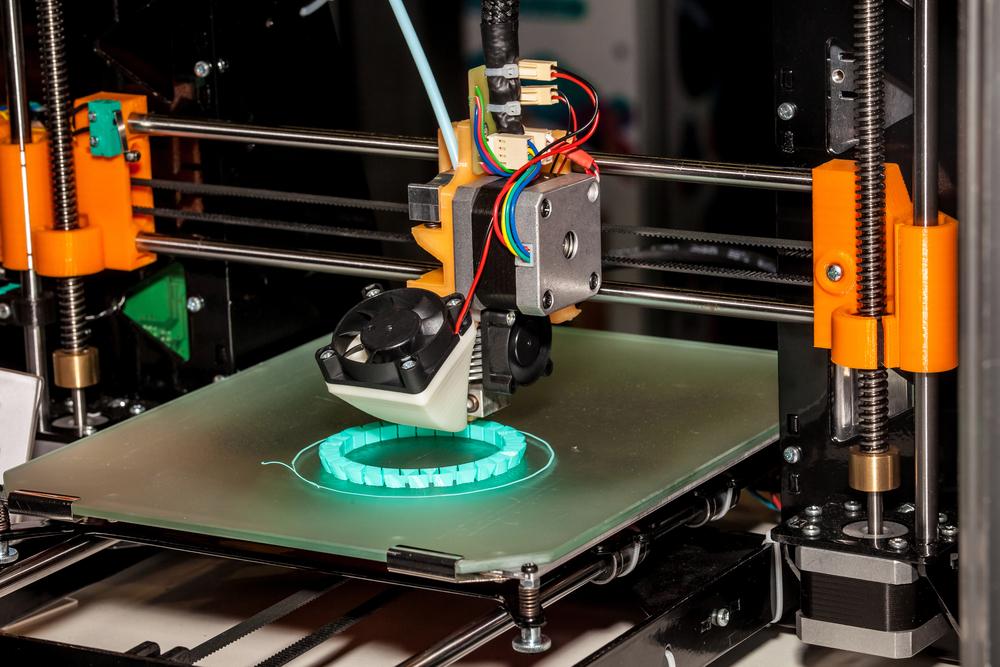
 Rapid Prototyping and 3D printing are often mistaken for being the same thing, however, there are some important differences.
Rapid Prototyping and 3D printing are often mistaken for being the same thing, however, there are some important differences.
Rapid Prototyping
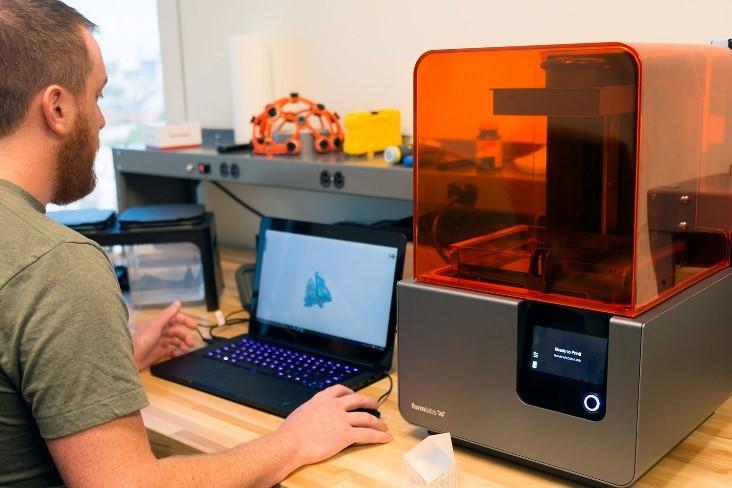
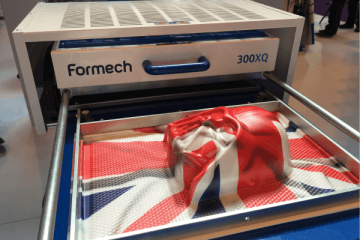
Rapid prototyping is the process of quickly building a 3D object to visually, and functionally, evaluate a design. There are several popular methods to choose from to rapidly prototype an object including vacuum casting, CNC machining and 3D printing to name a few. There are two categories within rapid prototyping:
- Low-fidelity prototypes: this is when the prototype has noticeable differentiations to the proposed final product.
- High-fidelity prototypes: this is when the prototype matches the proposed final product.
Applications:
Rapid prototyping processes are largely used by product designers and engineers. This is because it enables them to physically view how their product will appear or work in the early stages of design.
Having a physical model is also beneficial for clients who are working with designers, as it allows them to comprehend each aspect of the product in context. As a result, clients are generally able to provide designers with more accurate feedback because they can see and touch it. This gives room for alterations and improvements to be made in the early stages.
Jumping the gun straight into mass manufacturing is asking for a headache, especially due to the fact that fixing errors or making alterations at this late stage takes a lot of time and money. Rapid prototyping offers fantastic precision and is used to create accurate model geometries. It is an affordable way to test your product and we encourage everyone to make use of it!
3D Printing
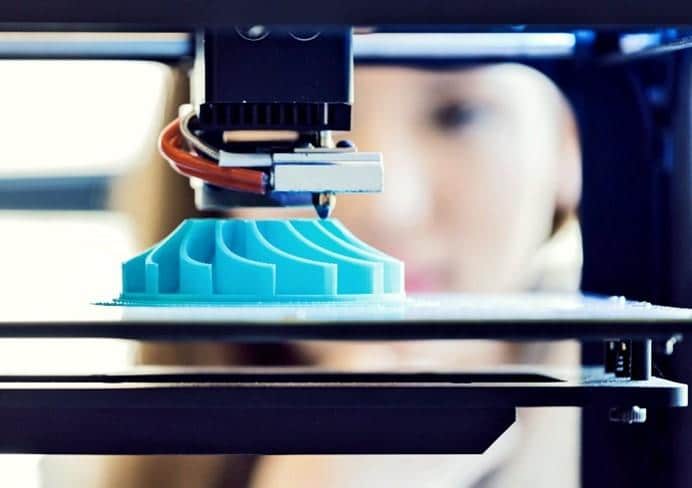
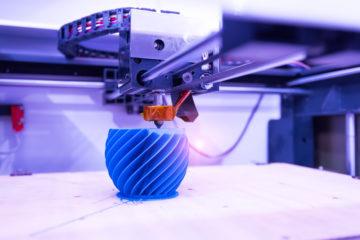
3D printing is a type of additive manufacturing process. Additive manufacturing describes the technology that is used to build 3D objects. As its name implies, it involves adding material layer-upon-layer to create an object.
By contrast, traditional manufacturing processes are subtractive – such as carving, milling, and machining. In additive manufacturing, computer-aided-design (CAD) directs data to hardware that can physically add material in layers to form precise geometries. 3D printing is one of several types of additive manufacturing processes.
Applications:
It is becoming more prominent for 3D printing to be used in manufacturing as an additive process. There are a growing number of companies employing this on a large scale. You might be wondering – why use 3D printers for this? Well, 3D printers offer the opportunity to create complex parts that would otherwise be too difficult or expensive to manufacture using traditional dies, moulds, milling, or machining. With intricate features and complex part geometries becoming feasible to manufacture, really the sky is the limit for 3D printing.
Other advantages include a reduction in assembly pieces. In contrast to traditional methods of joining multiple pieces together, you can now 3D print all of your pieces as a single part, which can increase strength and durability. 3D printing can make a part weight lighter and reduce waste drastically. In fact, it can reduce waste by up to 90% compared to using traditional subtractive manufacturing methods.
Aerospace Companies
Key applications include environmental control systems (ECS) ducting, custom cosmetic aircraft interior components, rocket engines components, combustor liners, tooling for composites, oil and fuel tanks and UAV components.
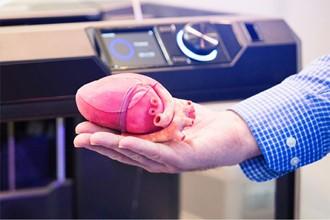
Medical Industry
Key applications include true-to-life anatomical models, orthopaedic implant devices, dental devices, pre-surgery models from CT scans, custom saw and drill guides, enclosures, and specialized instrumentation.
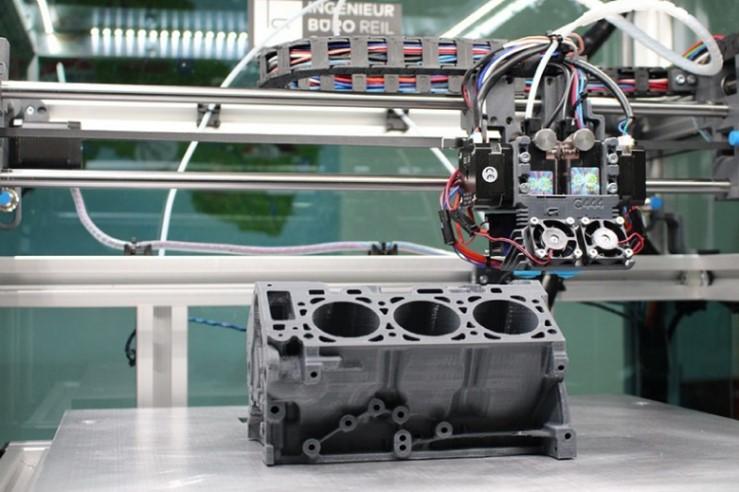
Transportation Industry
Key applications include complex ductwork that can’t be fabricated with conventional manufacturing methods, elastomeric models, grilles, custom interior features and large panelling.
Gas, Oil and Energy Industry
Key applications include rotors, stators, turbine nozzles, fluid/water flow analysis, flow meter parts, mud motor models, pressure gauge pieces, control-valve components, and pump manifolds.
At Dienamics, rapid prototyping plays a pivotal role in the development of products. For more information on how we can help bring your ideas to life, contact us today!
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Get the latest news from Dienamics into your inbox