Industrial design, like technology, is constantly changing and evolving. Not only because of advancements in the technology and processes, but also because of the changing demands within the industry and from consumers.
These ‘advancements’ usually mean the streamlining of processes, and also improvements to productivity.
The phrase uttered often in recent years is “Better-faster-cheaper”, and while the three don’t always go hand-in-hand, these 4 industrial design trends making a mark in 2018 could mean big things for the industry.
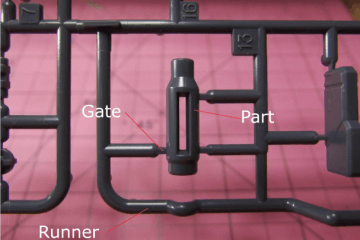
1. 3D printing
We’ve all heard of the incredible things being produced by 3D printers, from lawnmowers to Vincent van Gogh ear, but the real benefit from 3D printing is in prototyping.
For the most part, 3D printing is still too expensive and time consuming for mass production, but it can assist with product prototyping, as it allows you to create objects from 3D imaging or design blueprints.
This being said, 3D printing is slowly making the transition from producing prototypes and visual aids to being capable of manufacturing end-user parts. It’s only a matter of time and further developments in the technology.
2. IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) still causing some head scratching, but it has big ramifications for the industry.
What does IoT actually mean? Essentially, the Internet of Things is the concept of connecting any device with an on and off switch to the Internet (and/or to each other). This includes everything from cellphones, coffee makers, washing machines, lamps, and almost anything else you can think of. It means all of these “things” can be connected to the internet and then also communicate with each other.
The IoT in the design and manufacturing industry will bring together an entire ecosystem of communication between equipment, devices, and sensors, which could mean easier recording of primary information and generating analytics and answers in real time.
While the Internet of Things seems like a concept for the distant future, it’s much closer than you think.
3. The Cloud
Some describe “The Cloud” simply as: the Internet, but there is more to it than that. The Cloud involves using the internet to utilise software or services, without the need to physically download or install them.
Think of something like Microsoft Word, it’s software that you need to install in your computer. Google Docs on the other hand offers the same properties, but doesn’t require you to download and install anything, instead you use it online and your files are stored in an online server.
Cloud-based services offer flexibility, automatic updates, enhanced collaboration, time and cost savings, and minimal upfront investments for design and manufacturing software.
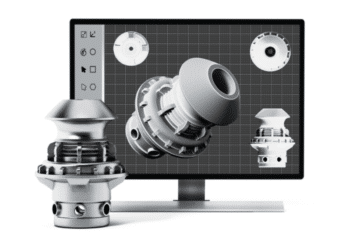
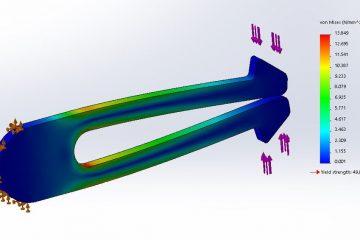
4. The growth of Computer-Aided Engineering
Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) refers to the use of software and automation to design better parts and products. CAE is incredibly helpful in the product development process, from design and virtual testing with sophisticated analytical algorithms to the planning of manufacturing.
The testing and simulation analysis of CAE means less physical prototyping, which not only cuts down on material usage and labour, but also speeds up the prototyping process dramatically.
For a long time, the use of complex CAE was reserved for large companies with sophisticated IT infrastructure, but as the software becomes easier to use and access (particularly with the help of Cloud computing), smaller and more diverse businesses are using it to streamline their product development process.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Get the latest news from Dienamics into your inbox