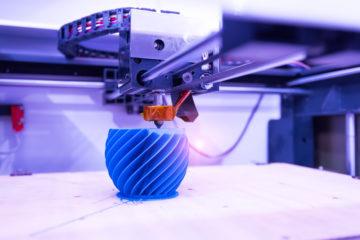
Rapid prototyping is the process by which tangible, physical objects are manufactured using free-form fabrication. Rapid prototyping had its inception in the 1980’s.
While it was initially used to create product models, today rapid prototyping is used to create many different types of products, reported The B.L.G.A. Blog.
Range of application
Rapid prototyping is associated with the creation of models or prototypes in the design stage. However, rapid prototyping can be used to create completely usable, durable parts for final use.
In these cases, the final parts are produced on a small production scale, as the technology yields smaller quantities by nature. In art, rapid prototyping has been used to create fine or delicate shapes with intricate parts that feature as elements in sculptures.
Computer technology
Computer programs are used to digitise the process, resulting in high accuracy both in the design and actual production stages, as virtual designs can be more accurate than non-digital designs.
Design systems
Rapid prototyping design systems can be categorised as being formative or summative. Formative systems alternate cycles of design and testing to refine the product. This can result in a higher quality product, but it can be a more expensive and time-consuming exercise.
Summative design systems or processes involve a test at the end of the design process, which means there are only two major steps in the process. While this can mean a faster turnout and fewer costs, it can leave less time for designers and engineers to fine-tune the design.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Get the latest news from Dienamics into your inbox