A lot of people go through life with no real interest in the ‘behind the scenes’ stuff. They don’t want to know where their dinner came from, they just want to know it’s in front of them. They have a similar opinion on everything from how their car works to the physics that drive our reality. There is nothing wrong with this kind of person, it takes all kinds to make up the world. There is another type of person, however, and this type of person likes to know the back story of everything. This type of curious individual loves watching documentaries about how things are built, behind-the-scenes features on how certain films are shot, and is usually the type of person who takes things apart to find out on their own what makes it tick. It if for these inquisitive creatures that we’ve created this article, a brief look at the way in which plastic injection moulding works. While most of our homes are filled with items that came into existence through plastic injection moulding, many of us have no idea how it works. Allow us to explain…
Manufacturing Process
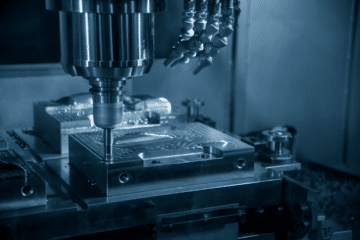
Basically, injection moulding requires whatever material (plastic, in this case) to travel through a heated barrel (thus liquefying it) and then into a pre-made mould wherein it hardens again. While this is an industrial engineering and manufacturing process, it has a lot in common with the art of pastry cooking! Scoff though you may, the principles of heating a material and then injecting it into a mould for it to set conjures up many an image of culinary art.
Materials
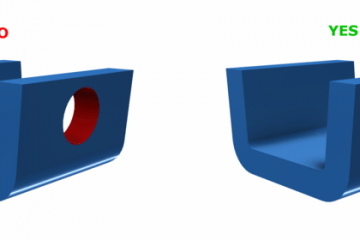
The material used in plastic injection moulding is thermoplastic. Thermoplastic is a polymer, and it is also known as thermosoftening plastic because of the softening effect heat has on the material. The properties of thermoplastic allow it to liquefy at an elevated temperature and then set into a solid once it cools. The exciting thing about thermoplastics is that they can repeat the melting/freezing process many times, making them valuable for a wide range of uses, especially when it comes to injection moulding.
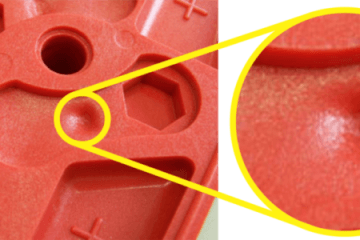
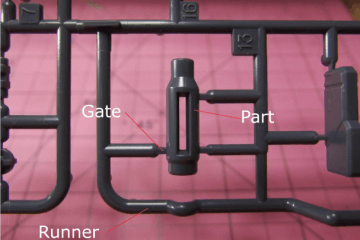
There are several parties involved in the manufacturing of goods through plastic injection moulding. The moulds themselves are created by mould makers out of metal, and the product design is conducted by industrial designers or engineers. At this stage the injection moulding takes place, and the soft plastic is driven through to the mould by a plunger-like part.
From entire bodies of vehicles to tiny little buttons, plastic injection moulding is responsible for many of the products we see every day.
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Get the latest news from Dienamics into your inbox